Nuclear medicine combines chemistry, physics, mathematics, computer technology, and medical science. Nuclear medicine has invented new methods and approaches for diagnosing and treating diseases, enabling doctors and specialists to observe the internal activities of the patient’s body in molecular detail with minimal damage and complications. In this way, the accuracy and precision of the diagnosis and planning for the patient’s treatment become much more efficient. If your doctor has suggested a method of nuclear medicine for a better diagnosis or if you are curious about the field of nuclear medicine, we recommend you follow us in the rest of this article.
What is nuclear medicine?
Nuclear medicine is the technology of using radiopharmaceuticals and radioactive tracers to observe the inner workings of the human body. Radiopharmaceuticals and radioactive tracers (radiotracers) are radioactive products that help doctors and specialists to diagnose and evaluate the problem, disease, or internal disorder of the patient’s body more accurately, efficiently, and quickly. In addition, these products have many uses for the treatment of diseases.
In nuclear medicine methods, such as radioactive scanning, tiny amounts of radiotracers enter the patient’s body through injection, ingestion, or inhalation of a safe gas and accumulate in the target area. Then the specialist takes pictures of the patient’s affected area using special devices. Nuclear medicine-based tests are helpful for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of various diseases, including:
- Cancer ;
- heart disease ;
- digestive diseases ;
- endocrine disorders ;
- Neurological disorders.
Since X-rays pass through soft tissue such as muscles and blood vessels, imaging and viewing these areas becomes difficult without a material that increases the image’s contrast. Radioactive materials act as a contrast agent and improve the clarity and accuracy of the photos. In this way, the specialist can diagnose the disease in the early stages, limit the treatment to specific cells and monitor the patient’s body’s response to the treatment.
Applications of nuclear medicine technology
Nuclear medicine is used to evaluate, diagnose and treat many conditions. Some of the applications of nuclear medicine are diagnosis and evaluation of response to treatment of important diseases, such as:
- Types of cancer ;
- Abnormalities of internal organs;
- narrowing of vessels and channels;
- Congenital disorders in babies and children;
- internal inflammations and infections;
- Evaluation of recurrence of tumor types.
Other applications of nuclear medicine technology are evaluating and diagnosing infectious and inflammatory problems in bones, joints, and internal organs such as gall bladder and thyroid, adrenal glands, and blood cell disorders.
The role of nuclear medicine in diagnosing and evaluating the treatment of heart, lung, and brain problems
Nuclear medicine technology can make the process of diagnosis and initiation of treatment much faster and easier with minimal side effects when examining the body’s vital organs, such as the heart, lungs, brain, and kidneys. For example, for a vital organ such as the heart, special nuclear medicine devices can provide such facilities:
- Assessment of heart function and blood flow;
- Investigating coronary artery disease and the degree of coronary artery stenosis;
- Assessment of damage to the heart after a heart attack ;
- Choosing the best treatment option, such as heart bypass surgery and angioplasty;
- Evaluation of the results of vascular opening methods;
- Examination of heart transplant withdrawal;
- Analysis of heart function before and after chemotherapy.
Lung scans to find breathing problems, diagnosis of the need for a lung transplant, and the patient’s body response to the transplant are some of the benefits of nuclear medicine for another vital organ of the body, the lungs.
Also, the field of nuclear medicine has taken an essential step for the early examination of brain abnormalities in patients suffering from seizures and Alzheimer’s, identification of damaged areas of the brain, study of abnormalities in patients suspected of Parkinson’s disease or other movement disorders, as well as diagnosis of the best place for biopsy (sampling).
Most of these diagnoses are made with the help of two widely used imaging methods based on nuclear medicine, i.e., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET). In the following, we will learn more about the performance of these methods.
How to prepare for nuclear medicine procedures?
You don’t need to worry if your doctor has suggested a procedure like nuclear imaging. In this section, we will explain the necessary points for you.
- You may be asked to wear unique clothing to protect against radiation. Sometimes, you can do an imaging test in your regular clothes.
- In case of pregnancy or breastfeeding, inform the doctor or technician.
- Give your doctor or technician a list of all the medications you take. These medicines include all vitamins and herbal supplements.
- Tell your doctor or technician about any allergies, recent illnesses, or any other medical or health problems you have.
- As much as possible, please do not bring your jewelry, decorative and metal items or remove them before the photo shoot. These objects may interfere with the imaging process.
- The doctor or technician will explain how to prepare for the examination.
- Remember to ask the specialist or imaging technician questions about any issues that cause confusion or concern.
Nuclear medical equipment
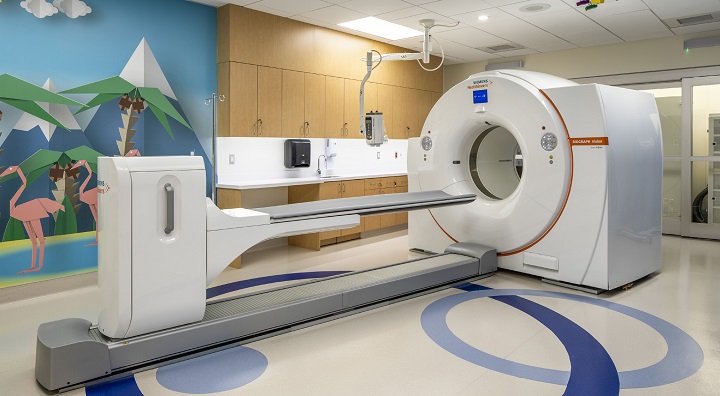 Nuclear medicine imaging is performed with gamma, SPECT, and PET cameras, similar to a CT or MRI machine. These cameras do not emit radiation and can only detect the energy and gamma rays produced by radioactive substances in the patient’s body and convert them into images. You must lie on a unique bed between two parallel gamma cameras for imaging.
Nuclear medicine imaging is performed with gamma, SPECT, and PET cameras, similar to a CT or MRI machine. These cameras do not emit radiation and can only detect the energy and gamma rays produced by radioactive substances in the patient’s body and convert them into images. You must lie on a unique bed between two parallel gamma cameras for imaging.
Gamma cameras are in specific frames and connected to a round, donut-shaped gate. The cameras may rotate around your body during imaging to capture more detail and clarity in the 3D images.
How are imaging and treatment done in nuclear medicine?
To perform nuclear medicine procedures, radioactive medicinal substances (radiotracers) enter the body through injection, swallowing, or gas inhalation.
- In testing and imaging, radiotracers are collected in a specific organ or attached to particular cells in the body. The rays and energy emitted from the target area are detected and recorded in imaging devices such as gamma cameras. Radiotracers show the rate of metabolism and heat (warmth or coldness) of some body regions. The radiotracer accumulates in hot areas, and cold areas indicate less concentration and activity. The images are finally recorded and processed by the computer.
- In radiotherapy treatment ( RIT ), the particular substance of monoclonal antibody (monoclonal antibody), which is made to treat and fight cancer cells, is paired with radiopharmaceuticals. After moving in the body towards the treatment cells, they help to transfer high-dose radiation therapy directly to the intended area, such as the area where the tumor is located.
Your doctor may ask you to stay in the hospital or do it on an outpatient basis to perform tests, imaging, or treatment procedures. In the following, we mention what you may experience during the process. Before starting, we must emphasize that the various methods based on nuclear medicine are generally painless and do not cause any particular complications.
Procedures for nuclear medicine procedures
- First, you lie on a unique table, and the nurse or technician injects the radiopharmaceutical or radiotracer into a vein in your hand. You may also be asked to swallow a capsule or liquid or inhale a gas. These substances are usually odorless and tasteless and will not cause problems.
- Apart from the feeling of the needle entering the vein, you will not feel any particular pain during the injection. You may also feel a cold liquid coming up from a vein in your arm. There is no need to worry; you will not have any particular problems.
- Some tests may require a nurse or technician to insert a catheter into your bladder, which may cause temporary discomfort.
- The time required for the accumulation of radiopharmaceutical or radiotracer in the body depends on the type of process and may last from a few seconds to a few days. The doctor or technician will explain the special conditions of the process and its duration.
- During the imaging, a special camera may rotate around your body, or the specialists may ask you to change your position and posture.
- You will need to remain still for a short time during the process.
- Because the camera may get too close to you to capture better quality images, tell your doctor or technician if you fear confined spaces.
- If your child is being tested, the doctor may use a small amount of sedation to keep the child from moving. In this case, the doctor or technician will let you know if your child can eat anything on the test day.
Patient experience after the test
- After the test, you may be asked to wait for a while so that more images can be taken if needed.
- You can usually resume your normal daily activities after the test. Of course, the doctor or nurse may ask you to stay hospitalized longer. However, your doctor or technician will give you the necessary instructions.
- Most of the radioactive material is excreted from the body after a few hours through urine or feces. You can also drink a lot of water to flush the radioactive material out of your body faster.
- After the treatment sessions with radioactive materials, you may need to follow some tips. These items will be notified to you by the technician or nurse.
- If you are going through the treatment process with radiopharmaceuticals, you can ask your doctor about the side effects of the drug in question. Side effects are temporary, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or fatigue.
Advantages and disadvantages of nuclear medicine
In many cases, the methods used in nuclear medicine provide the doctor and specialist with unique information that cannot be obtained with other tests and imaging. Therefore, diagnosing and assessing the extent of the disease or disorder becomes much easier and faster.
In addition, nuclear medicine scans and images often replace exploratory biopsies and surgeries to diagnose internal problems. So, the inner pain and discomfort of the patient are determined with much less cost and side effects. Also, most nuclear medicine methods provide more detailed information than exploratory surgeries.
PET scans based on nuclear medicine provide the specialist with specific information for planning the course of radiation therapy.
Radionuclide treatments also target cancer cells and limit radiation damage to healthy tissue. Also, compared to other treatment methods, they have fewer side effects and shorter periods.
Complications of nuclear medicine
In nuclear medicine, only a tiny dose of radioactive material is used, which can have much more benefits than other methods. Doctors have used atomic medicine technology’s diagnostic and therapeutic methods for over six decades. So far, no long-term adverse effects of exposure to this small dose of radioactive materials have been reported.
Allergic reactions to radiopharmaceuticals and radiotracers are usually infrequent and mild. For example, injection of radiopharmaceuticals or radiotracers may cause mild pain and redness. This problem is often resolved very quickly. Perhaps the main disadvantage of nuclear medicine methods and processes is their time-consuming nature. Some of these procedures may take several hours to several days. Some newer equipment has made these processes much shorter.
In general, numerous researches count the advantages of nuclear medicine methods much more than their disadvantages or problems. However, you can discuss all your issues and sensitivities with the doctor and ask questions about any worries or concerns regarding these procedures. Especially if you are breastfeeding a baby or there is a possibility of pregnancy, be sure to inform the doctor and the technician before the course.
last word
Nuclear medicine is a combination of different fields and sciences, such as chemistry, physics, mathematics, and medicine, which uses tiny amounts of radioactive materials to carry out the necessary processes of diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of internal diseases. Using nuclear medicine, doctors and specialists can see the details of possible diseases and disorders down to the molecular level and do better planning for targeted treatment with a faster and more accurate diagnosis. Therefore, the development and expansion of methods based on the field of nuclear medicine can be a revolution in health care and increase the hope of recovery for patients and their relatives.
Warning! This article is only for educational purposes; to use it, it is necessary to consult a doctor or specialist.



