Some languages look terrifying to us Farsi speakers, especially East Asian languages. Some of these languages, like Korean, are easy and only look deceiving, but others are as difficult as they look. Japanese is in the second category and is considered one of the most challenging languages. In the following, we will get to know this language and its structure, and then we will examine the reason for the difficulty of the Japanese language. Note that other factors, such as motivation and persistence, play a role in determining your difficulty level with a language.
Is learning Japanese difficult?
The answer to this question is entirely up to you. Overall, Japanese is one of the most challenging languages to master, especially for English speakers. However, no one-size-fits-all answer to this question applies to all language learners. To help you find the answer to your question, we take a closer look at this language and its structure. After reading this article and knowing the generality of this language, you can decide to learn it with a more open mind. Consider other factors for the final decision. For example, how many hours a day do you spend learning a language, and how motivated are you?
Familiarity with the Japanese language
With more than 127 million speakers worldwide, Japanese is one of the most crucial living languages in the world. This language is in the category of isolated languages and has no connection with other languages. This language is the only living language in the world for which no relatives have been found yet. Some hypotheses relate this language to the Korean language, and others consider it a subset of South Asian languages such as Austroasiatic and Austronesian. Among the Austroasiatic languages, we can mention Vietnamese; among the Austronesian languages, we can mention Indonesian, Malay, and Filipino.
1. Writing system
The Japanese language has three writing systems: hiragana, Katakana, and kanji. HiragKatakanaKatakana is the phonetic Katakana of this language, and the exciting thing about them is how they are pronounced. Unlike English, where vowels are pronounced differently in different situations, the Japanese phonetic alphabet (Hiragana and Katakana) is always written and read similarly. Of course, there is another system called Romaji, which is the Latin writing system of this language.
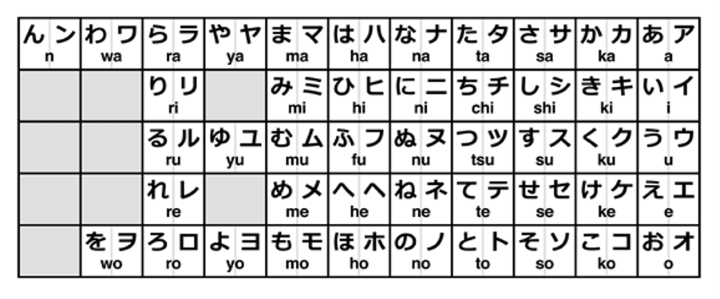
1. Hiragana and Katakana
Hiragana and Katakana, also known as Katakanakana, actually translate the syllables of the Japanese language into written form. The best way to learn both is to use a suitable table to practice writing with while reading your writing out loud. Maybe this writing system is strange, but we promise it will not be challenging to learn. Learning hiragana and Katakana is mandatory, but Katakananately, these two writings are similar. The difference between katakana and hiragana isKatakanar usage. Katakana is mainly used for foreign words and emphasis in writing, but hiragana is more widely used and taught in schools. It is not difficult to distinguish hiragana from Katakana and vice versa. Katakana is more curved, and Katakana is angular. In Katakanaowing, you can see a table of kana, where the right side of each house on the table is Katakana, and the left side is katakanaragana
2. Kanji
Kanji is more complicated than kana. This writing system is based on Chinese characters. Each kanji symbol may have a different pronunciation but the same meaning. The first question for most language learners is how many letters are in the Japanese language. First, we must say that the Japanese alphabet has the same symbols, and we don’t have anything called the Japanese alphabet. There are thousands of kanji, the exact number of which is unknown. It is said that you need to remember more than 3,000 kanji to read intermediate-level texts! Learning kanji is one of the biggest challenges in learning Japanese. If you plan to be in Japan briefly, you can skip learning kanji. But if you are serious about learning Japanese and aiming to master it, you should spend a lot of time on kanji.
2. phonetics
Phonetics is another problematic topic in Japanese. The pronunciation of some sounds, such as ぢ, pronounced between di and ji, does not exist in our language. Japanese pronunciation is a little more straightforward if you are fluent in Spanish or other languages emphasizing vowels. In Japanese phonetics, you should be familiar with two words, flood and mura.
Mura is a unit of syllables similar to that used in Japanese. Mura and Silab play a vital role in accents and dialects. Sound hyphenation occurs in every mora, and how hyphenation is used may change the meaning of the word. For example, the monosyllabic word kan means “official” if it is read with a low sound and “feels” if it is read with a low sound. The best way to learn Japanese sounds is through practice and repetition. After you know the correct pronunciation of each sound, memorize and repeat it along with kana.
3. Dialects
You will come across different dialects in Japanese, but you don’t need to master them all. Japanese dialects are very different, and if you are fluent in one dialect, you probably won’t understand the other. Therefore, several dialects are considered to create more integration. Among these dialects, we can mention the common dialect, or Kyotsugu, and the standard dialect, or Hyojungo, based on the Tokyo dialect. Of course, you will also have other options, such as the Kansai dialect, which is mainly used informally.
4. grammar
The first interesting thing about Japanese grammar is that it has remained the same for centuries, has not changed much, and is relatively simple. Japanese grammar uses the order of subject + object + verb, or SOV. Therefore, learning Japanese grammar is tricky for English speakers with SVO orders. Still, this issue will not be so challenging for Persian speakers with a structure similar to Japanese.
Sentence changes are mostly done on the verb, which is one reason for the simplicity of Japanese grammar. Japanese words have no gender or number and are used similarly. Also, in Japanese, we only have present and past tense. Of course, there are other modes, but they are not as tricky as the grammar of different languages, such as English.
Note that there are strict rules for formality and respect in this language. For example, if a person addresses his boss, his sentence changes.
you say
Learning Japanese probably takes more time and energy than learning other languages. Learning kana and pronouncing syllabaries is easy, grammar is not so tricky, and kanji is complicated. Learning a new language is difficult but possible, and the key to success is practice and persistence.
Now that you know this language, do you think Japanese is difficult?



