The placenta is one of the vital organs during pregnancy, and its position inside the uterus is critical. An ectopic placenta occurs when all or part of the placenta is in the path of entry into the uterus. Do you know why this happens and what complications and treatment it has? Stay with us until the article’s end to learn more about the pair.
What is a pair of waypoints?
Placenta is an organ that establishes communication between the mother and fetus during pregnancy. This organ provides oxygen and nutrients needed by the fetus and removes waste materials. The placenta is connected to the fetus through the umbilical cord. Usually, the placenta attaches to the upper part of the side of the inner wall of the uterus. Placenta previa is one of the problems during pregnancy, and it happens when all or part of the placenta is placed in the lower part of the uterus and covers the uterus entrance. This issue can cause bleeding during pregnancy, delivery, or after. There is a possibility of placenta previa in one out of every 200 pregnancies.
Changes in the uterus and placenta can cause problems that usually resolve on their own. Otherwise, the fetus will be born by cesarean section .
Types of pairs of waypoints
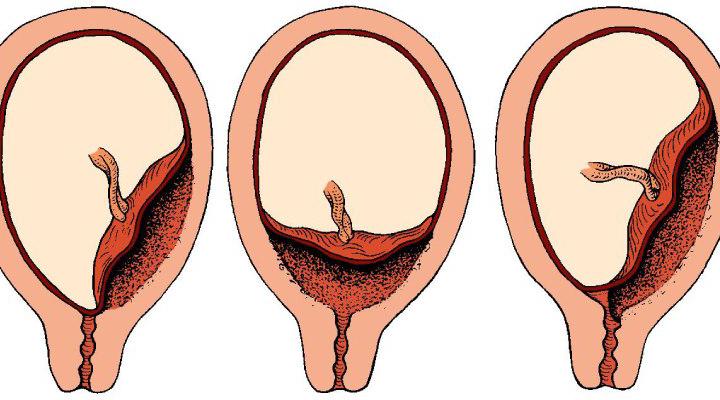
- Marginal placenta: It touches the cervix’s edge but does not cover it. This type of placenta previa usually resolves itself before delivery.
- Partial placenta: The placenta covers part of the cervix.
- Complete placenta: The placenta completely covers the cervix and blocks the vagina. This type of placenta rarely resolves on its own.
Any placenta may cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth. Due to the increased possibility of bleeding, most people need a cesarean delivery.
The cause of placenta previa
Placenta previa is more common in some women, including:
- People with children;
- People with a history of previous cesarean section;
- People with wounds in the uterus due to previous surgery;
- People with a history of placenta previa in a last pregnancy;
- People who have become pregnant with assisted reproductive methods ;
- multiple pregnancies;
- Age more than 35 years;
- smokers;
- people using cocaine;
- History of uterine fibroids.
The cause of bleeding caused by the placenta
- The cervix is located between the uterus and the vagina. At the end of pregnancy, the wall of the cervix becomes thin and prepares for childbirth. If the placenta is near the cervix, it can cause bleeding.
- During childbirth, the cervix is opened to expel the fetus. At this time, the blood vessels between the placenta and the uterus rupture and cause bleeding.
Symptoms of placenta previa
- The main symptom of placenta previa is vaginal bleeding with a light color, which is usually painless and occurs in the 20th week of pregnancy. This bleeding may stop and start again a few days later.
- Mild abdominal or back cramps.
Side effects of placenta
If you have placenta previa, your doctor will check you and your baby for side effects. In the following, we will examine some of the side effects of placenta previa.
- Bleeding: Severe vaginal bleeding or hemorrhaging may occur during pregnancy, delivery, and the first hours after delivery and may be life-threatening.
- Premature delivery: Heavy bleeding may cause immediate delivery before the end of the pregnancy period.
- Blood loss: Anemia, low blood pressure, paleness, or shortness of breath due to excessive blood loss.
- Placenta accreta: placenta accreta is associated with a group of diseases called placenta accreta. In this disease, the placenta grows into the uterine wall. Placenta accrete increases the risk of bleeding during pregnancy, delivery, or after.
- Detachment of the placenta: Detachment of the placenta before the birth of the baby can reduce the amount of oxygen and nutrients needed by the fetus.
Complications of the placenta for the fetus
- Premature baby: If the bleeding is heavy and you need a cesarean, a premature baby may be born.
- Low birth weight: Difficulty staying warm and weight gain are potential side effects of low birth weight.
- Breathing problems: Underdeveloped lungs may cause breathing problems.
Time to see a doctor
See a doctor if you have vaginal bleeding in the second and third-trimester pregnancy. If your bleeding is heavy, go to the emergency room.
Pathway pair detection
The ectopic placenta is detected by ultrasound. Most ectopic placentas are identified by ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy. Initial diagnosis is made with abdominal ultrasound, and intravaginal ultrasound is used for a more detailed examination.
Treatment of placental abruption
If placenta previa is detected during pregnancy with a routine ultrasound, you will need more ultrasounds to check for changes in the placenta. In most women, placenta previa is diagnosed early in pregnancy and resolves independently. The distance between the vagina and the placenta increases as the uterus grows. Therefore, the placenta is placed in a higher position inside the uterus, and its edges will be towards the vagina.
If the placenta problem is resolved, you can also think about having a natural delivery, and if it is not resolved, you should plan for a cesarean delivery.
Treatment of spontaneous placental bleeding
- Vaginal bleeding after 20 weeks of pregnancy is treated as a medical emergency. In this case, you should be transferred to the delivery room. The condition of you and the fetus will be checked, and you will receive units of blood to replace the lost blood.
- If you are 36 weeks pregnant, a cesarean section may be performed. If you have lost a lot of blood and your health or the fetus is at risk, a cesarean section may be performed before 36 weeks.
- If you have bleeding for the first time and it stops in less than 48 hours, you may be discharged from the hospital. But if the bleeding is heavy and continuous, you may be hospitalized.
Treatment of placenta previa without bleeding
If you are not bleeding, the goal of treatment is to reduce the chance of bleeding and bring you to the delivery time. Your medical team may advise you to avoid certain activities, including:
- intercourse or sexual activity that causes orgasm;
- mild or vigorous exercise;
- lifting everyday or heavy objects;
- I have been standing for a long time.
If you go home after your first bleed, you may receive the same advice to reduce the chance of a second bleed. Also, even if you are not bleeding, you should probably plan for a cesarean at 36 to 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Other treatments
- rest at home or hospitalization;
- taking medicine to delay childbirth;
- Steroid injection for faster fetal lung growth;
- blood transfusion in severe bleeding;
- Immediate cesarean section for heavy and uncontrolled bleeding.
Difference between placenta previa and placental abruption
Ectopic placenta means the placenta partially or completely covers the opening of the cervix but is still attached to the uterine wall. Placental abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus. Both cases can cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth.
Difference between placenta previa and placenta previa
The placenta can be anywhere in the uterus. An anterior placenta is formed when the placenta attaches to the front wall of the uterus.
Does placental abruption cause miscarriage?
Miscarriage means the loss of a fetus before the 20th week. Usually, the placenta is not detected until the 20th week. For this reason, it does not seem that placental abruption causes miscarriage.
you say
How familiar are you with the pair? Have you ever had this problem? If you wish, you can write us your experience and opinion in the comments section and send this article to your friends through social networks.
Warning! This article is only for educational purposes; to use it, it is necessary to consult a doctor or specialist.



